What is craniosynostosis?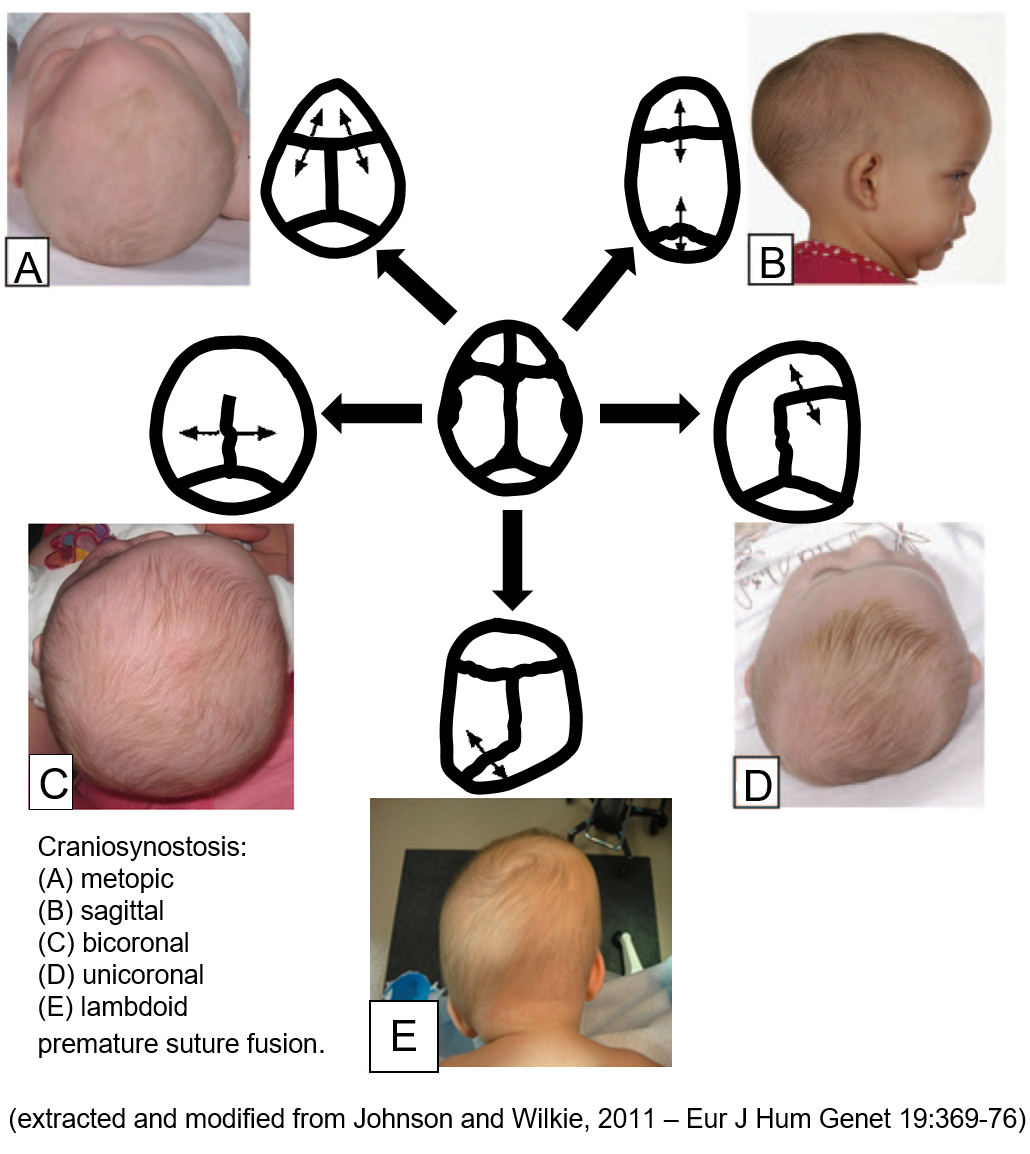
The mammalian cranial vault largely consists of five flat bones that are joined together along their edges by soft fibrous tissues called sutures. The sutures are designed to give the bones flexibility for birth and to allow the skull to expand and grow as the brain enlarges. Premature closure of the sutures, is a medical condition that occurs in about 1 in 2,000 births and is called craniosynostosis. Current treatments of this condition involves in majority of cases invasive surgery where by craniofacial surgeons reconstruct the skull. While treatments of some simple forms of this condition i.e. single suture fusion is relatively well established (while varied centre by centre across the world), treatment of some other forms of this condition are still challenging.
What do we do?
Our overall aim is to advance treatment of this condition. Over the past five years, we have been investigating the biomechanics of normal and craniosynostotic skull growth in mouse and human. This has involved various experimental measurements and developing advance computer simulations. These have allowed us to predict the radial expansion of the skull and bone formation at the sutures that occur hand in hand during the postnatal development. These developments have now set the foundation for a validated computational platform to predict the outcome of surgical treatment for this condition with the long term vision of optimizing treatment of this condition.
